Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology converts printed, handwritten, or scanned documents into machine-readable and structured data. By applying advanced image processing and artificial intelligence techniques, OCR systems automate the extraction of information from unstructured sources, such as PDFs, photos, invoices, contracts, and forms.
This capability allows organizations to eliminate manual data entry, integrate extracted data into digital workflows, and reduce errors caused by human interpretation.
What is OCR and how it works
OCR is the process of transforming visual representations of text, such as those found in images or scanned files, into digital characters that can be stored, searched, edited, and processed programmatically.
The process typically involves the following technical stages:
1. Image Preprocessing
Before recognition, images are enhanced to improve readability. This step may involve grayscale conversion, noise reduction, skew correction, binarization, and contrast normalization.
2. Layout Analysis
The system detects and segments the content into logical components such as text blocks, lines, tables, and images. This is critical for preserving the structure of complex documents.
3. Character Recognition
OCR engines use pattern recognition, convolutional neural networks (CNNs), and natural language processing (NLP) to detect and classify characters. Some systems also support multiple languages, font styles, and handwritten text.
4. Post-processing and Validation
The recognized text is cleaned, validated, and structured. AI-based models use contextual clues and dictionaries to correct errors and format data into standardized outputs such as JSON, XML, or CSV.
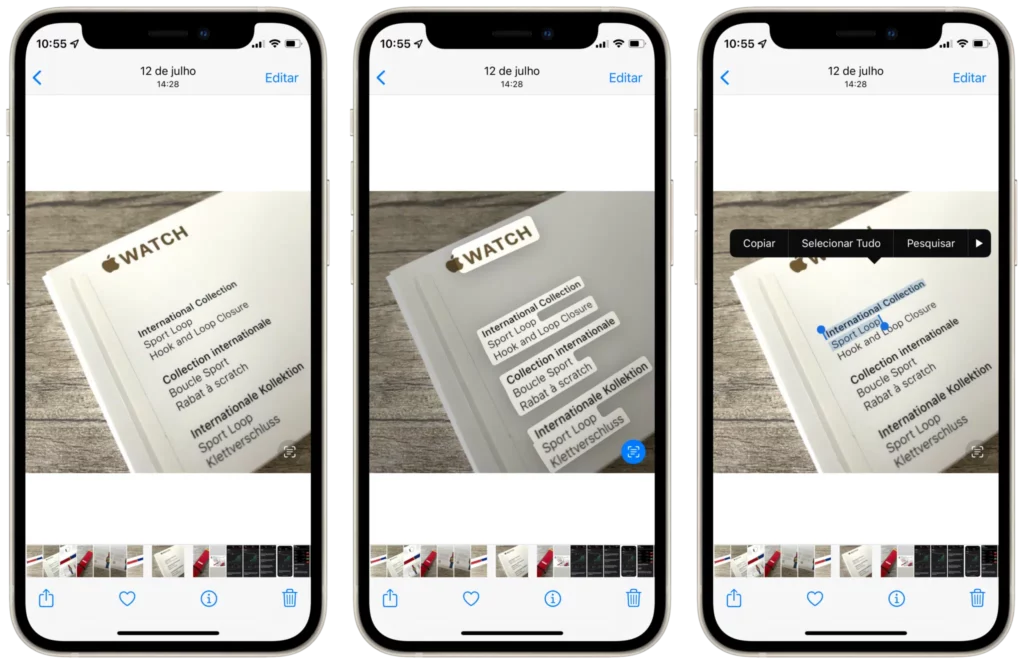
Source: Mac Magazine
Benefits of implementing OCR in business workflows
OCR offers significant operational advantages across various industries. It can reduce the manual data entry workload by up to 95% and accelerate processing time from hours to minutes.
The technology improves accuracy through automated validation and contextual analysis, and it is highly scalable, able to process large volumes of documents concurrently. Additionally, OCR integrates with APIs, databases, and enterprise systems, enabling real-time updates and enhanced regulatory compliance through digital audit trails and structured storage.
Applications of OCR across business domains
OCR is a technology with diverse applications, including Invoice Processing, Contract Analysis, Receipt and Expense Management, Form Digitization, and Archive Digitization. It works by enabling computers to “read” and extract information from documents, converting them from a printed or handwritten format into digital data.
Invoice Processing: This involves extracting key information like vendor details, invoice numbers, dates, line items, taxes, and totals to automate accounts payable workflows. This significantly reduces processing time at scale.
Contract Analysis: The technology identifies and extracts critical clauses, parties, renewal dates, signatures, and legal references, which is vital for legal review and risk management.
Receipt and Expense Management: It helps parse receipt data, such as the merchant’s name, transaction amount, tax breakdown, and payment method, to enable automated reimbursement and expense tracking.
Form Digitization: This application converts structured forms (like those for HR, medical, and onboarding) into normalized databases. It can handle both printed and handwritten input fields.
Archive Digitization: Finally, OCR transforms physical archives into searchable digital repositories, allowing for metadata tagging, indexing, and full-text search across legacy documents.
Challenges of traditional OCR tools
Older systems for text recognition, while capable of handling basic tasks, often lack the adaptability, accuracy, and integration needed for today’s businesses. Their limitations include a low tolerance for poor-quality scans or complex document layouts, and they typically rely on rigid, template-based configurations that require manual setup.
These systems also struggle to adapt to varying document formats and offer minimal support for real-time integrations with other platforms. To get past these challenges, many companies are now using advanced platforms that leverage AI, computer vision, and intelligent automation.
Parser: AI-Powered document processing at scale
Parser is an advanced document automation platform that combines OCR with artificial intelligence to deliver highly accurate data extraction from any document format. Key features include:
High Accuracy Recognition
Achieves up to 99 percent accuracy using deep learning models and contextual language processing.
Support for All Formats
Handles PDFs, scanned documents, images (JPG, PNG, TIFF), Word documents, spreadsheets, and structured formats like XML or JSON.
Custom Data Extraction
Define custom templates, fields, validation rules, and output structures tailored to your business needs.
API-First Integration
Robust RESTful API and real-time webhooks enable direct integration with ERP systems, CRMs, and internal databases.
Data Privacy and Security
Documents are processed securely and automatically deleted after seven days. No data is used for model training, and clients can request deletion at any time.
Rapid Deployment
Set up and start automating in under five minutes. Parser includes 10 free credits to test the platform on real documents before making any financial commitment.
Technical integration and data security
The Parser platform is designed to operate as a core part of a wider automation ecosystem. Its technical integration capabilities include a RESTful API with comprehensive documentation, customizable endpoints for tailored data outputs, and webhooks for real-time data transmission. The platform also supports both synchronous and asynchronous processing, along with auto-sync and bidirectional data updates with internal systems.
Regarding security and compliance, Parser is built with enterprise-grade data protection. All documents are automatically deleted after seven days, and data is never stored for AI training. The platform uses a SOC-compliant infrastructure and secure data centers, giving users full control over the data lifecycle and access management.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What types of documents does Parser support?
Parser supports PDFs, scanned images, Word files, Excel spreadsheets, forms, and other structured or unstructured formats.
Can Parser extract specific data fields?
Yes. You can define which fields you want to extract, apply validation rules, and receive structured outputs tailored to your needs.
Is integration with my system possible?
Parser includes a modern API and webhook system, enabling seamless integration into existing software workflows, ERPs, or CRMs.
Is the data secure?
Parser adheres to strict security practices. Documents are automatically deleted after processing, and your data is never used for model training.
How long does it take to get started?
Initial setup takes less than 5 minutes. You can begin processing documents immediately using the 10 free credits available.
Start processing documents automatically
Parser enables organizations to automate data extraction, reduce processing times, and increase accuracy across all document types. With advanced AI, fast setup, and robust integration options, it is an ideal solution for teams looking to scale document processing without expanding operational overhead.
Visit Parser to create your account and start automating your workflow with 10 free credits. No credit card required.










